Model: JM272QE-144Hz


Key Features
- 27" IPS panel with 2560x1440 QHD Resolution
- MPRT 1ms Response Time and 95Hz Refresh Rate
- Display Port + HDMI connectors
- No stuttering or tearing with AMD FreeSync Technology
- The IPS panel brings the better visual angles
- FlickerFree and Low Blue Mode Technology
What is refresh rate?
The first thing we need to establish is “What exactly is refresh rate?” Fortunately it isn’t very complex. Refresh rate is simply the number of times a display refreshes the image it shows per second. You can understand this by comparing it to frame rate in films or games. If a film is shot at 24 frames per second (as is the cinema standard), then the source content only shows 24 different images per second. Similarly, a display with a display rate of 60Hz shows 60 “frames” per second. It’s not really frames, because the display will refresh 60 times each second even if not a single pixel changes, and the display only shows the source fed to it. However, the analogy is still an easy way to understand the core concept behind refresh rate. A higher refresh rate therefore means the ability to handle a higher frame rate. Just remember, that the display only shows the source fed to it, and therefore, a higher refresh rate may not improve your experience if your refresh rate is already higher than the frame rate of your source.
Why is it important?
When you connect your monitor to a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit/Graphics Card) the monitor will display whatever the GPU sends to it, at whatever frame rate it sends it, at or below the maximum frame rate of the monitor. Faster frame rates allow any motion to be rendered on screen more smoothly (Fig 1), with reduced motion blur. This is very important when watching fast video or games.
Refresh Rate and Gaming
All video games are rendered by computer hardware, no matter their platform or graphics. Mostly (particularly in the PC platform), the frames are spit out as quickly as they can be generated, because this usually translates to a smoother and nicer gameplay. There will be less delay between each individual frame and therefore less input lag.
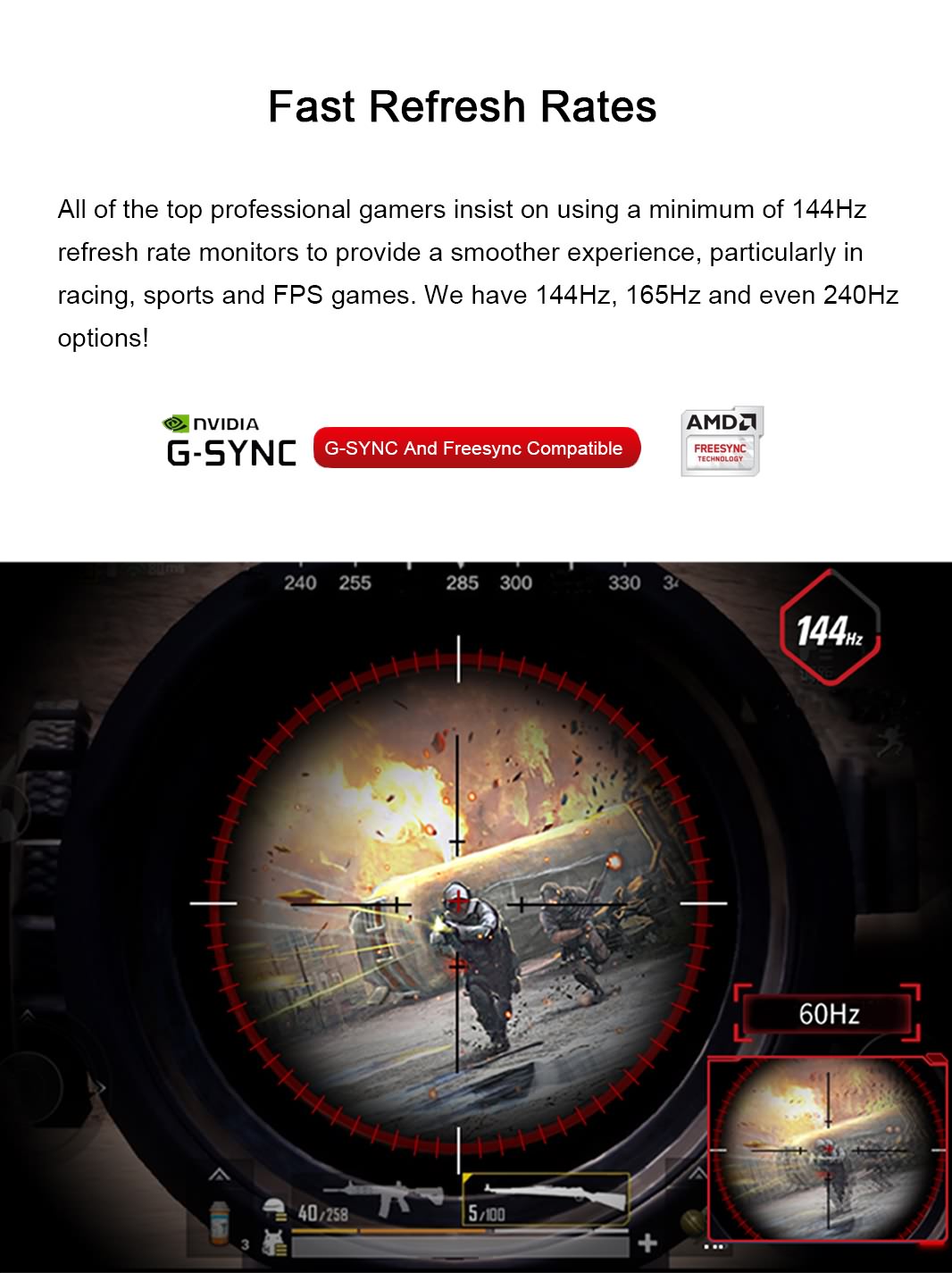
A problem that can occur sometimes is when the frames are being rendered faster than the rate at which the display refreshes. If you have a 60Hz display, which is being used to play a game rendering 75 frames per second, you may experience something called “screen tearing”. This happens because the display, which accepts input from the GPU at somewhat regular intervals, is likely to catch the hardware between frames. The result of this is screen tearing and jerky, uneven motion. Lots of games allow you to cap your frame rate, but this means that you’re not using your PC to its full ability. Why spend so much money on the latest and greatest components like GPUs and CPUs, RAM and SSD drives if you are going to cap their capabilities?
What is the solution to this, you may wonder? A higher refresh rate. This means either buying a 120Hz, 144Hz or a 165Hz computer monitor. These displays can handle up to 165 frames per second and the result is much smoother gameplay. Upgrading from 60Hz to 120Hz, 144Hz or 165Hz is a very noticeable difference. It is something that you just have to see for yourself, and you can’t do that by viewing a video of it on a 60Hz display.
Adaptive refresh rate, however, is a new cutting-edge technology that is becoming more and more popular. NVIDIA calls this G-SYNC, while AMD calls it FreeSync, but the core concept is the same. A display with G-SYNC will ask the graphics card how quickly it is delivering the frames, and adjusts the refresh rate accordingly. This will eliminate screen tearing at any frame rate up to the maximum refresh rate of the monitor. G-SYNC is a technology that NVIDIA charges a high licensing fee for and it can add hundreds of dollars to the price of the monitor. FreeSync on the other hand is an open source technology provided by AMD, and only adds a small amount to the cost of the monitor. We at Perfect Display install FreeSync on all of our gaming monitors as standard.
Should I buy a G-Sync and FreeSync compatible gaming monitor?
Generally speaking, Freesync is extremely important for gaming, not just for avoiding tearing but for insuring an overall smoother experience. This is especially true if you're running gaming hardware that's outputting more frames than your display can handle.
G-Sync and FreeSync are solutions to both of these issues by having the display refresh at the same pace as frames are rendered by the graphics card, resulting in smooth, tear-free gaming.


What is HDR?
High-dynamic range (HDR) displays create deeper contrasts by reproducing a higher dynamic range of luminosity. An HDR monitor can make highlights look brighter and deliver richer shadows. Upgrading your PC with an HDR monitor is worth it if you play video games with high-quality graphics or watch videos in HD resolution.
Without getting too deep into the technical details, an HDR display produces greater luminance and color depth than screens built to meet older standards.


1MS Response Time reduces ghosting & blurring while transitioning pixels, always keeping the enemy & terrain precisely in focus during chaotic moments.

10 Bit color output can represent between 0000000000 to 1111111111 in each of the red, blue, and yellow colors, meaning that one could represent 64x the colors of 8-bit. This can reproduce 1024x1024x1024 = 1,073,741,824 colors, which is an absolutely huge amount more colors than 8 bit. For this reason, many of the gradients in an image will look more smooth like in the image above, and 10 bit images are quite noticeably better looking than their 8-bit counterparts.














